43 histogram labels in r
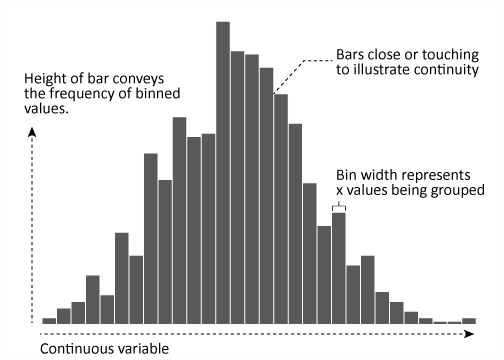
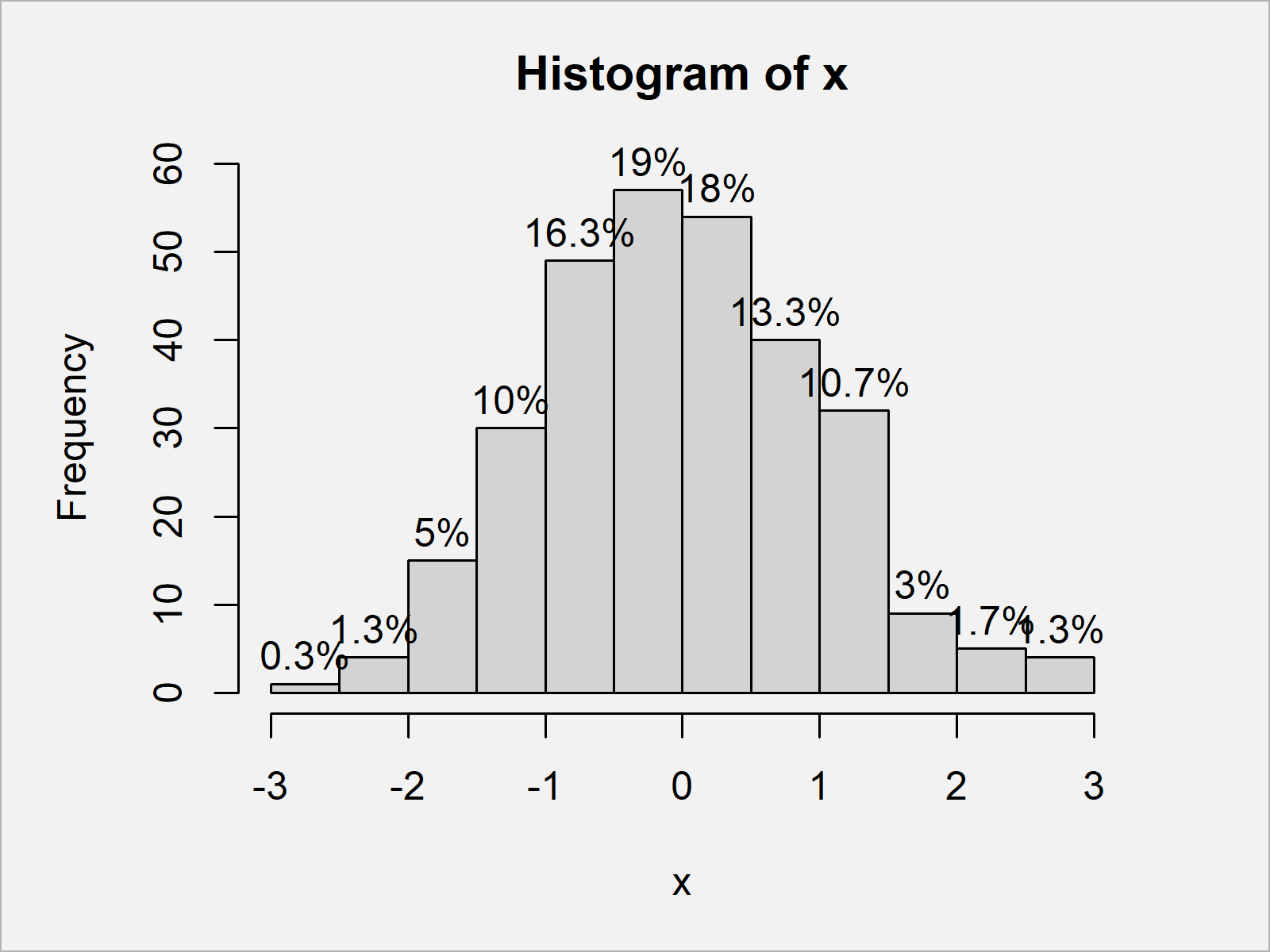
How to label histogram bars with data values or percents in R The example below is just slightly adapted from one on the hist() help page: hist(islands, col="gray", labels = TRUE, ylim=c(0, 45)) Getting percentages is a bit more involved. The only way I know to do that it to directly manipulate the object returned by a call to hist(), as described in a bit more detail in my answer to this similar question: Frequency histogram in R | R CHARTS A basic frequency histogram. The hist function allows creating histograms in base R. By default, the function will create a frequency histogram. # Sample data (exponential) set.seed(1) x <- rexp(400) # Histogram hist(x)
› r-bar-chart-histogramBar Chart & Histogram in R (with Example) - Guru99 Jul 16, 2022 · Step 2: Create a basic histogram; Step 3: Change the orientation; Step 4: Change the color; Step 5: Change the size; Step 6: Add labels to the graph; Step 1) Create a new variable. You create a data frame named data_histogram which simply returns the average miles per gallon by the number of cylinders in the car.
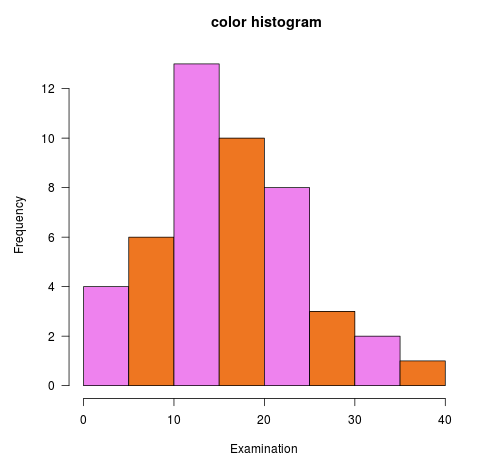
Histogram labels in r
Axes customization in R | R CHARTS It is possible to rotate the tick mark labels in several ways making use of the las argument. Option 1. Parallel to axis (default). plot(x, y, pch = 19, las = 0, main = "Parallel") Option 2. Horizontal. plot(x, y, pch = 19, las = 1, main = "Horizontal") Option 3. Perpendicular to axis. plot(x, y, pch = 19, las = 2, main = "Perpendicular") Option 4. How to Specify Histogram Breaks in R (With Examples) If you use the hist () function in R, Sturges' Rule will be used to automatically choose the number of bins to display in the histogram. hist (data) Even if you use the breaks argument to specify a different number of bins to use, R will only use this as a "suggestion" for how many bins to use. hist (data, breaks=7) Create a Histogram in Base R (8 Examples) | hist Function Tutorial As you can see based on the RStudio console output, the hist function returns a lot of information on our histogram, i.e. breaks, counts, density, mids, xname, equidist, and attr. You may have a look at the help documentation of the hist function to learn more about these information.
Histogram labels in r. Add Count and Percentage Labels on Top of Histogram Bars in R The hist() method in base R is used to display a histogram of the given data values. It takes as input a vector of the data values and outputs a corresponding histogram for the same. Syntax: hist ( x , labels) Parameter : x - The set of data points to plot; labels - By default, FALSE. If true, it is used to denote a set of counts on the top of bars. Setting the font, title, legend entries, and axis titles in R - Plotly Global and Local Font Specification. You can set the figure-wide font with the layout.font.family attribute, which will apply to all titles and tick labels, but this can be overridden for specific plot items like individual axes and legend titles etc. In the following figure, we set the figure-wide font to Courier New in blue, and then override ... statisticsglobe.com › ggplot2-histogram-in-r-geomCreate ggplot2 Histogram in R (7 Examples) | geom_histogram ... Figure 1: Basic ggplot2 Histogram in R. Figure 1 visualizes the output of the previous R syntax: A histogram in the typical design of the ggplot2 package. In the following examples I’ll explain how to modify this basic histogram representation. So keep on reading! Example 2: Main Title & Axis Labels of ggplot2 Histogram R - Histograms - tutorialspoint.com The basic syntax for creating a histogram using R is −. hist (v,main,xlab,xlim,ylim,breaks,col,border) Following is the description of the parameters used −. v is a vector containing numeric values used in histogram. main indicates title of the chart. col is used to set color of the bars. border is used to set border color of each bar.
How to Make Stunning Histograms in R: A Complete Guide with ggplot2 Scatter Plots with R. Boxplots with R. This article will show you how to make stunning histograms with R's ggplot2 library. We'll start with a brief introduction and theory behind histograms, just in case you're rusty on the subject. You'll then see how to create and tweak ggplot histograms taking them to new heights. › blog › histogram-r-ggplot2How to make a histogram in R with ggplot2 - Sharp Sight There are actually several ways to create a histogram in R. You can create an "old school" histogram in R with "Base R". Specifically, you can create a histogram in R with the hist () function. This is the old way to do things, and I strongly discourage it. The old school plotting functions for R are poorly designed. They're hard to use. R Histogram - Base Graph - Learn By Example In R, you can create a histogram using the hist() function. It has many options and arguments to control many things, such as bin size, labels, titles and colors. ... labels: If TRUE, draws labels on top of bars: density: The density of shading lines: angle: The slope of shading lines: col: A vector of colors for the bars: Histograms in R language - GeeksforGeeks We can create histogram in R Programming Language using hist() function. Syntax: hist(v, main, xlab, xlim, ylim, breaks, col, border) Parameters: v: This parameter contains numerical values used in histogram. main: This parameter main is the title of the chart. col: This parameter is used to set color of the bars. xlab: This parameter is the label for horizontal axis.
› histogram-in-rLearn How to Create a Histogram Using R Software - EDUCBA R uses hist () function to create histograms. This hist () function uses a vector of values to plot the histogram. Histogram comprises of an x-axis range of continuous values, y-axis plots frequent values of data in the x-axis with bars of variations of heights. Syntax: The syntax for creating histogram is [R] Histogram Label Font Size - ETH Z [R] Histogram Label Font Size Robert Baer rbaer at atsu.edu Mon Apr 14 22:40:54 CEST 2008. Previous message: [R] Histogram Label Font Size Next message: [R] how to add different type of lines (short dash, long dash) into current plot) Messages sorted by: R hist() to Create Histograms (With Numerous Examples) - DataMentor Example 3: Use Histogram return values for labels using text () h <- hist (Temperature,ylim=c (0,40)) text (h$mids,h$counts,labels=h$counts, adj=c (0.5, -0.5)) Defining the Number of Breaks With the breaks argument we can specify the number of cells we want in the histogram. However, this number is just a suggestion. how to add data labels to geom_histogram - RStudio Community below is my code. ggplot (data,mapping=aes (x=Annualized.Sick.Days,y=..count..,label=..count..,fill=Direct.Indirect))+. geom_histogram (binwidth=10,color="white")+. scale_x_continuous (breaks = seq (30, 100, 10), lim = c (30, 100))+. theme_classic2 () +.
Add custom tick mark labels to a plot in R software Change the string rotation of tick mark labels The following steps can be used : Hide x and y axis Add tick marks using the axis () R function Add tick mark labels using the text () function The argument srt can be used to modify the text rotation in degrees.
Data Visualization with R - Histogram - Rsquared Academy Set labels to TRUE. Method 2 Specify the label values in a character vector. Putting it all together.. Before we end this post, let us add a title and axis labels to the histogram. hist (mtcars$mpg, labels = TRUE, prob = TRUE , ylim = c ( 0, 0.1 ), xlab = 'Miles Per Gallon' , main = 'Distribution of Miles Per Gallon' , col = rainbow ( 5 ))
Labels in Histograms - RStudio Community amount_of_sugar_in_cakes = rnorm (1000,37,5) hist (amount_of_sugar_in_cakes, labels = TRUE, xlab = "Amount of Sugar in Cake grams", ylab = "Number of Cakes", breaks=100, main = "Distribution of Sugar in Cakes: You Dislike Anything with more than 27 grams of Sugar") Does anyone know why the labels on the x-axis and the y-axis are not showing up?
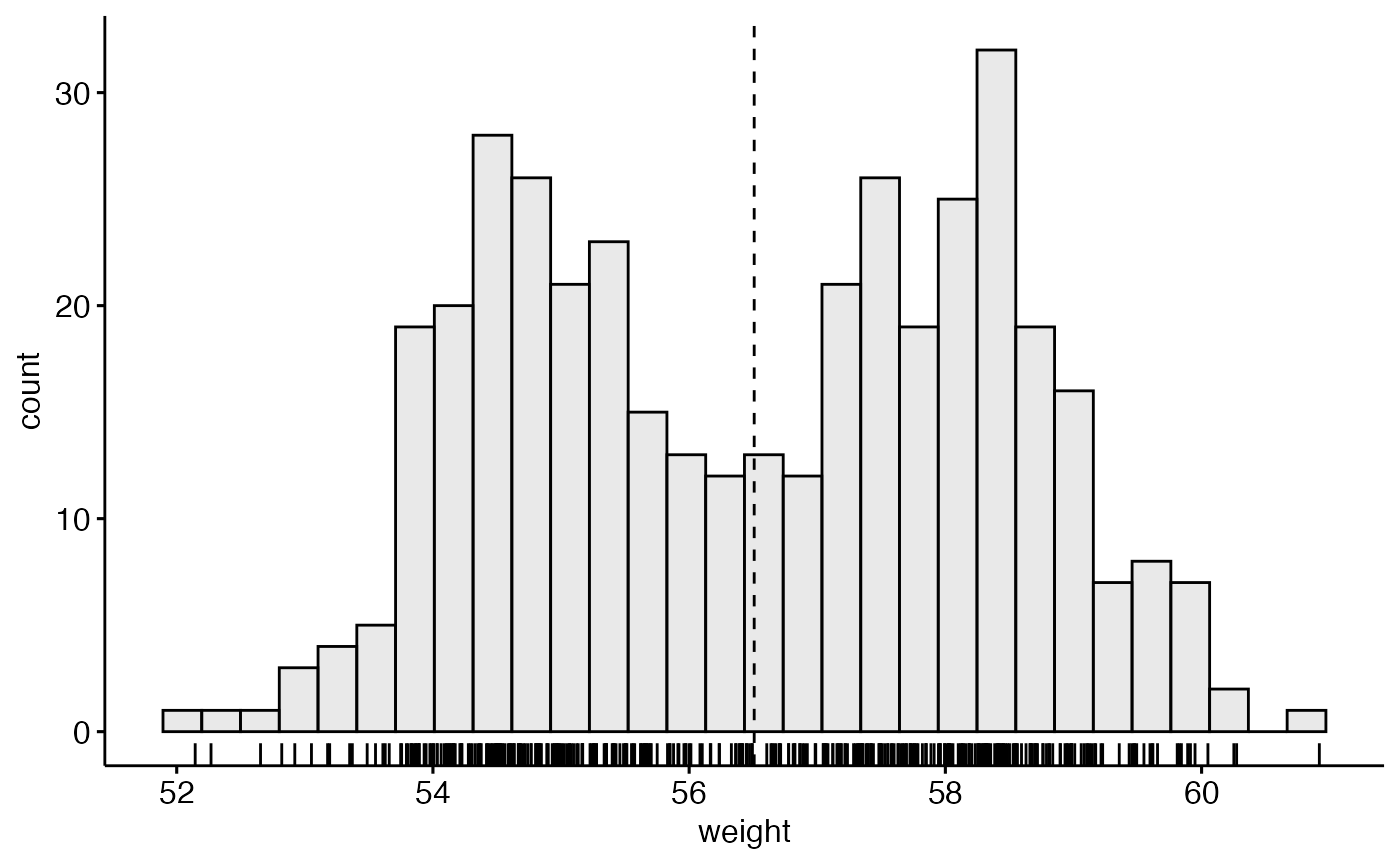
ggplot2 histogram plot : Quick start guide - R software and data ... GGPlot2 Essentials for Great Data Visualization in R Prepare the data The data below will be used : set.seed(1234) df <- data.frame( sex=factor(rep(c("F", "M"), each=200)), weight=round(c(rnorm(200, mean=55, sd=5), rnorm(200, mean=65, sd=5))) ) head(df) ## sex weight ## 1 F 49 ## 2 F 56 ## 3 F 60 ## 4 F 43 ## 5 F 57 ## 6 F 58 Basic histogram plots
Histogram in R Programming - Tutorial Gateway and the complex syntax behind this to make a Histogram in r is: hist(x, breaks = "Sturges", freq = NULL, probability = !freq, xlim = range(breaks), ylim = NULL, col = NULL, angle = 45, include.lowest = TRUE, right = TRUE, density = NULL, main = NULL, xlab = xname, ylab, border = NULL, axes = TRUE, plot = TRUE, labels = FALSE, nclass = NULL, warn.unused = TRUE,..)
statsandr.com › blog › graphics-in-r-with-ggplot2Graphics in R with ggplot2 - Stats and R To keep it short, graphics in R can be done in three ways, via the: {graphics} package (the base graphics in R, loaded by default) {lattice} package which adds more functionalities to the base package. {ggplot2} package (which needs to be installed and loaded beforehand) The {graphics} package comes with a large choice of plots (such as plot ...
Histograms in R - Plotly How to make a histogram in R. New to Plotly? Plotly is a free and open-source graphing library for R. We recommend you read our Getting Started guide for the latest installation or upgrade instructions, then move on to our Plotly Fundamentals tutorials or dive straight in to some Basic Charts tutorials.
› r-programming › plot-functionR plot() Function (Add Titles, Labels, Change Colors and ... The most used plotting function in R programming is the plot() function. It is a generic function, meaning, it has many methods which are called according to the type of object passed to plot() . In the simplest case, we can pass in a vector and we will get a scatter plot of magnitude vs index.
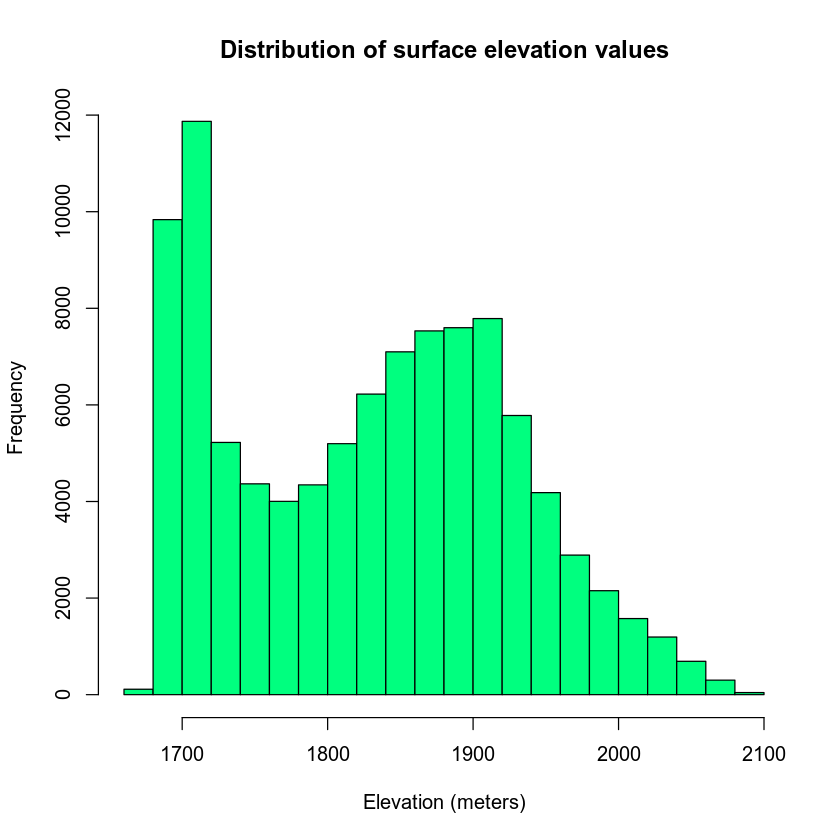
HISTOGRAM in R ⚡ [CREATE, CUSTOMIZE, BINS, ADD CURVES, ...] You can plot a histogram in R with the histfunction. By default, the function will create a frequency histogram. hist(distance, main = "Frequency histogram") # Frequency However, if you set the argument probto TRUE, you will get a density histogram. hist(distance, prob = TRUE, main = "Density histogram") # Density
How to apply manually created x-axis labels in a histogram created by ... Therefore, firstly we need to create the histogram by ignoring the labels and then axis function can be used for new values. Consider the below vector x and create a histogram of x by ignoring x-axis labels −. Example set.seed(1999) x<-rnorm(5000,9,1) hist(x,xaxt='n') Output. Now adding new values for x-axis labels −. Example
r-charts.com › distribution › histogram-group-ggplot2Histogram by group in ggplot2 | R CHARTS Create a grouped histogram in ggplot2, change the color of the borders and the fill colors by group and customize the legend of the plot. ... Custom legend labels.
How to Make a Histogram with Basic R | R-bloggers hist(AirPassengers, las=1) #Histogram of the AirPassengers dataset with the y-values projected horizontally According to whichever option you choose, the placement of the label will differ: if you choose 0, the label will always be parallel to the axis (which is the default); If you choose 1, the label will be put horizontally.

Add Count & Percentage Labels on Top of Histogram Bars in R (Example) | hist, paste0, round & length
Lattice Histogram in R - Tutorial Gateway The Lattice Histogram in R is useful to visualize the statistical information. Though it looks like Barplot, Histograms display data in equal intervals. Let us see how to Create a Lattice Histogram using the lattice library, Format its color, adding labels, and drawing multiple Histograms. Lattice Histogram in R syntax
hist function - RDocumentation If right = TRUE (default), the histogram cells are intervals of the form (a, b], i.e., they include their right-hand endpoint, but not their left one, with the exception of the first cell when include.lowest is TRUE. For right = FALSE, the intervals are of the form [a, b) , and include.lowest means ' include highest '.
Create a Histogram in Base R (8 Examples) | hist Function Tutorial As you can see based on the RStudio console output, the hist function returns a lot of information on our histogram, i.e. breaks, counts, density, mids, xname, equidist, and attr. You may have a look at the help documentation of the hist function to learn more about these information.
How to Specify Histogram Breaks in R (With Examples) If you use the hist () function in R, Sturges' Rule will be used to automatically choose the number of bins to display in the histogram. hist (data) Even if you use the breaks argument to specify a different number of bins to use, R will only use this as a "suggestion" for how many bins to use. hist (data, breaks=7)
Axes customization in R | R CHARTS It is possible to rotate the tick mark labels in several ways making use of the las argument. Option 1. Parallel to axis (default). plot(x, y, pch = 19, las = 0, main = "Parallel") Option 2. Horizontal. plot(x, y, pch = 19, las = 1, main = "Horizontal") Option 3. Perpendicular to axis. plot(x, y, pch = 19, las = 2, main = "Perpendicular") Option 4.























Post a Comment for "43 histogram labels in r"