43 bacteria cell with labels
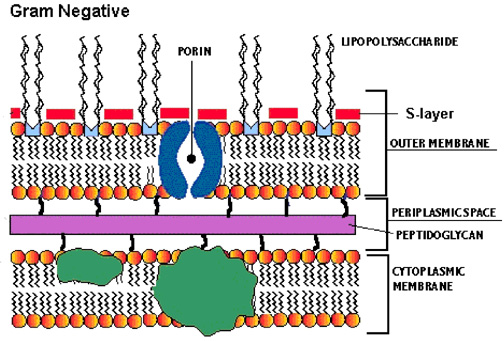
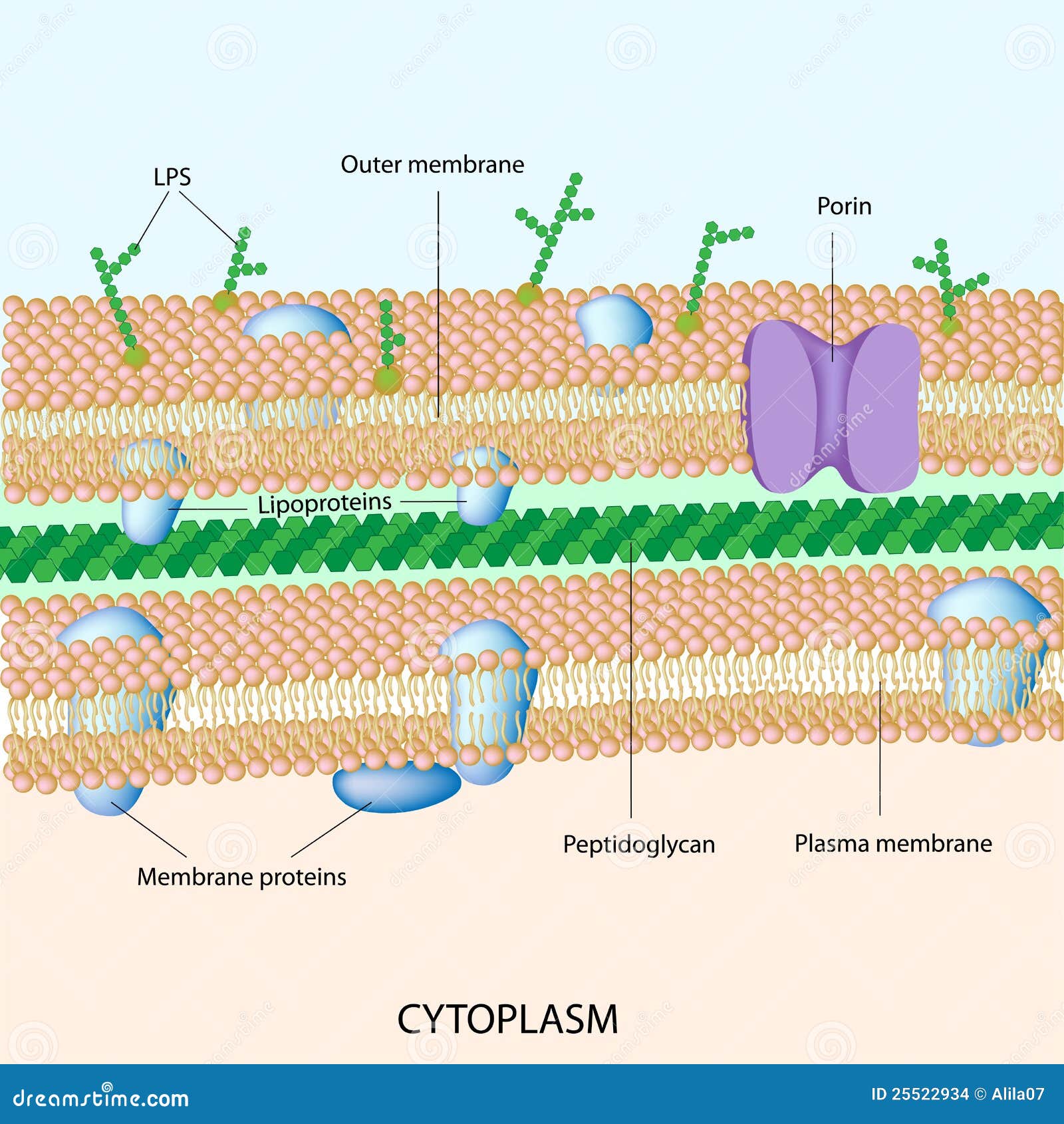
Bacterial Cytoplasm & Cell Membrane: Structure & Components Proteins, amino acids, sugars, nucleotides, salts, vitamins, enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, and internal bacterial structures all float around the cell in the cytoplasm. All of these components are vital... Technical pipeline for screening microbial communities as a function of ... B. cellulosilyticus grown on AcGGM) at 24 h (blue) and 72 h (green) compared to the unlabelled substrate (red). e Histogram indicating the shift in fluorescence observed for cells grown on labelled...
› a-to-z-guides › manuka-honeyManuka Honey: Medicinal Uses, Benefits, and Side Effects Feb 20, 2021 · Honey protects the body against damage caused by bacteria. Some honeys also boost production of special cells that can repair tissue damaged by infection. Manuka honey has an anti-inflammatory ...
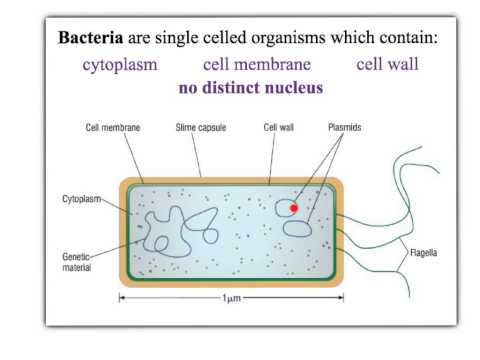
Bacteria cell with labels
Structure and Function of a Typical Bacterial Cell with Diagram August 14, 2021. Bacteria are unicellular. Their structure is a very simple type. Bacteria are prokaryotes because they do not have a well-formed nucleus. A typical bacterial cell is structurally very similar to a plant cell. The cell structure of a bacterial cell consists of a complex membrane and membrane-bound protoplast. Bacterial Cell Morphology and Classification: Definition, Shapes ... A bacteria that lives as one cell all alone is called a single cell. Some bacteria remain grouped together after cell division. A bacteria that lives in pairs has a diplo arrangement, with 'di-'... Bacteria - Definition, Structure, Diagram, Classification Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms with the absence of the nucleus and other c ell organelles; hence, they are classified as prokaryotic organisms. They are also very versatile organisms, surviving in extremely inhospitable conditions. Such organisms are called extremophiles.
Bacteria cell with labels. › jking540 › cell-biology-pptCell Biology ppt - SlideShare Sep 16, 2014 · Chapter 4 Section 2 Introduction to Cells Prokaryotic Cells -Cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles -Includes bacteria -Single, circular chromosome in nucleoid region -Surrounded by cell membrane and a cell wall made up of peptidoglycan -Divided into two domains, I.e., Archaea and Bacteria Animal Cell Diagram with Label and Explanation: Cell Structure, Functions Animal cell is a typical Eukaryotic cell enclosed by a plasma membrane containing nucleus and organelles which lack cell walls, unlike all other Eukaryotic cells. The typical cell ranges in size between 1-100 micrometers. The lack of cell walls enabled the animal cells to develop a greater diversity of cell types. Flagella: Structure, Arrangement, Function - Microbe Online Flagella (singular, flagellum) are the locomotory structures of many prokaryotes. The flagellum functions by rotation to push or pull the cell through a liquid medium. Bacterial Flagella Structure Arrangement and Types Functions of Bacterial Flagella Archaeal Flagella Protozoa Having Flagella Bacterial Flagella Various shapes and arrangements of Bacterial cells Bacteria are the ubiquitous microscopic organisms that are not visible with the naked eye. Bacterial morphology (size, shape and arrangement of bacterial cells) is one of the mostly used feature for the differentiation of various bacterial species.
Quiz: Trivia Question On Bacteria Cell Structure - ProProfs A. Flagella B. Chromosomal DNA C. Ribosomes D. Plasma Membrane 2. Which bacteria cell part goes in the box labelled b? A. Flagella B. Chromosomal DNA C. Ribosomes D. Cell Wall 3. Which bacteria cell part goes in the box labelled with the star? A. Flagella B. Chromosomal DNA C. Plasmid DNA D. Cell Wall 4. In situ food-borne pathogen sensors in a nanoconfined space by surface ... There are two SERS configurations for bacteria and virus detection, namely unlabeled or labeled SERS, as shown in Scheme 1. In label-free detection, bacterial cells and viruses or their metabolites can be directly introduced onto the nanostructures surface. Bacterial Growth Curve and Different Phases Therefore, the Bacterial growth curve consists of 4 different phases such as the lag phase, the exponential or logarithmic phase, stationary phase, and death or decline phase. Between each of these phases, there is a transitional period (curved portion). This represents the time required before all cells enter the new phase. Bacterial Capsule: Importance, Capsulated Bacteria - Microbe Online Capsule (also known as K antigen) is a major virulence factor of bacteria, e.g. all of the principal pathogens which cause pneumonia and meningitis, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria meningitidis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, and group B streptococci have polysaccharide capsules on their surface.
Bacteria Cell Label - how to make a prokaryotic bacteria cell model ... Bacteria Cell Label - 17 images - e coli bacteria animation stock video clip k001 2397, metabolic markers accurately diagnose typhoid fever, cell structure and function ap biology, 32 label the bacterial cell labels database 2020, An inside look at a biofilm: Pseudomonas aeruginosa flagella ... The opportunistic pathogen, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a flagellated bacterium, is one of the top model organisms for biofilm studies. To elucidate the location of bacterial flagella throughout the biofilm life cycle, we developed a new flagella biotracking tool. Bacterial flagella were site-specifically labeled via genetic code expansion. Bacterial capsule: compositions, structure, function The term bacterial capsule (Fig. 1) means a series of components positioned outside the bacterial cell wall. They are the components of the bacterial wall itself that often contribute to the capsule's formation. The bacterial capsule is not present in all bacteria but only in some of them. IT's All About A Bacterial Cell! - ProProfs Quiz The outermost layer of a bacterial cell is called the _____ 6. When you collected bacteria from around the school, their main source of food was: A. Particles in the air contained within the petri dish. B. Other microbes that were brought into the dish with the bacteria sample. C. Organic material that followed them from where they were ...
Tuberculosis Bacteria Cell | Free Images at Clker.com - vector clip art online, royalty free ...
Research Guides: BIO 2410: Microbiology: Microscopic Morphology What bacterial structure can be seen at the label 1? What stain was used to stain these bacteria? Structure 2A A1 Flagella A2 The bacteria with the flagella are unstained, the stained bacteria are added to the slide to help find the bacteria with the flagella.
Bacterial Cell Structure and Function - Pharmapproach.com Bacteria (singular: bacterium) are prokaryotic, generally unicellular organisms, which exist as single cells or as cell clusters. They are among the organisms that are too small to be visible to the naked eye. Thus, they can only be seen with the aid of a microscope.
Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) - Genome.gov Definition. The plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable.
High-throughput identification and quantification of single bacterial ... The bacterial microbiota works as a community that consists of many individual organisms, i.e., cells. To fully understand the function of bacterial microbiota, individual cells must be identified ...
Bacterial Identification | 8 Methods & Tests In Microbiology Even some bacteria have two flagella one on each side of the cell. By Cultural characteristics. Here bacteria are identified as group or culture as a whole and not individual bacteria. Since most bacteria grow in colonies and also divide fast, they can be easily grown into a culture in suitable nutrition media.
Bacteria - Wikipedia Bacteria (/ b æ k ˈ t ɪər i ə / (); common noun bacteria, singular bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell.They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms.Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats.
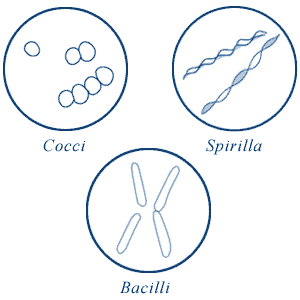
Different Size, Shape and Arrangement of Bacterial Cells Bacilli (or bacillus for a single cell) are rod-shaped bacteria. Spirilla (or spirillum for a single cell) are curved bacteria which can range from a gently curved shape to a corkscrew-like spiral. Many spirilla are rigid and capable of movement. A special group of spirilla known as spirochetes are long, slender, and flexible. Arrangement of Cocci
Bacteria - Definition, Structure, Diagram, Classification Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms with the absence of the nucleus and other c ell organelles; hence, they are classified as prokaryotic organisms. They are also very versatile organisms, surviving in extremely inhospitable conditions. Such organisms are called extremophiles.
Bacterial Cell Morphology and Classification: Definition, Shapes ... A bacteria that lives as one cell all alone is called a single cell. Some bacteria remain grouped together after cell division. A bacteria that lives in pairs has a diplo arrangement, with 'di-'...
Structure and Function of a Typical Bacterial Cell with Diagram August 14, 2021. Bacteria are unicellular. Their structure is a very simple type. Bacteria are prokaryotes because they do not have a well-formed nucleus. A typical bacterial cell is structurally very similar to a plant cell. The cell structure of a bacterial cell consists of a complex membrane and membrane-bound protoplast.







Post a Comment for "43 bacteria cell with labels"